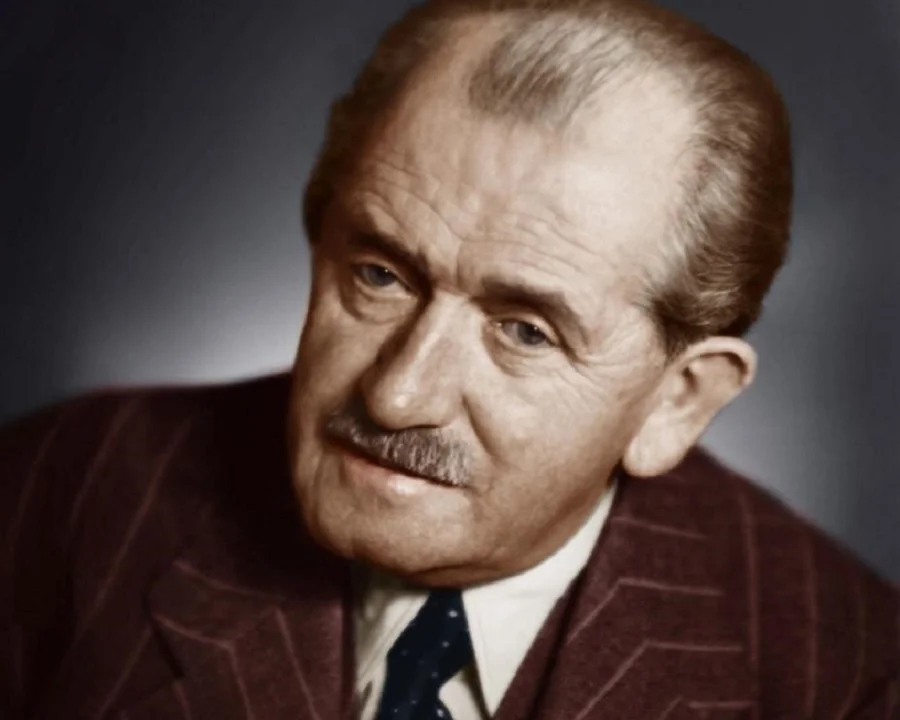

Ferdinand Porsche: Pioneering the Future of Automotive Engineering
Ferdinand Porsche, born on September 3, 1875, in Maffersdorf, Austria-Hungary (now Vratislavice nad Nisou, Czech Republic), was a pioneering automotive engineer and founder of one of the most iconic automobile manufacturers in the world. His remarkable contributions to the automotive industry and his innovative designs have left an indelible mark on the history of transportation.
Early Life and Education.
Ferdinand Porsche was born into a humble family with a strong mechanical inclination. From a young age, he displayed an extraordinary aptitude for mechanics and engineering. His father, Anton Porsche, was a skilled tinsmith, which provided a conducive environment for Ferdinand to learn and develop his mechanical skills. During his early years, he apprenticed at various mechanical and engineering firms, honing his talents and gaining practical knowledge.
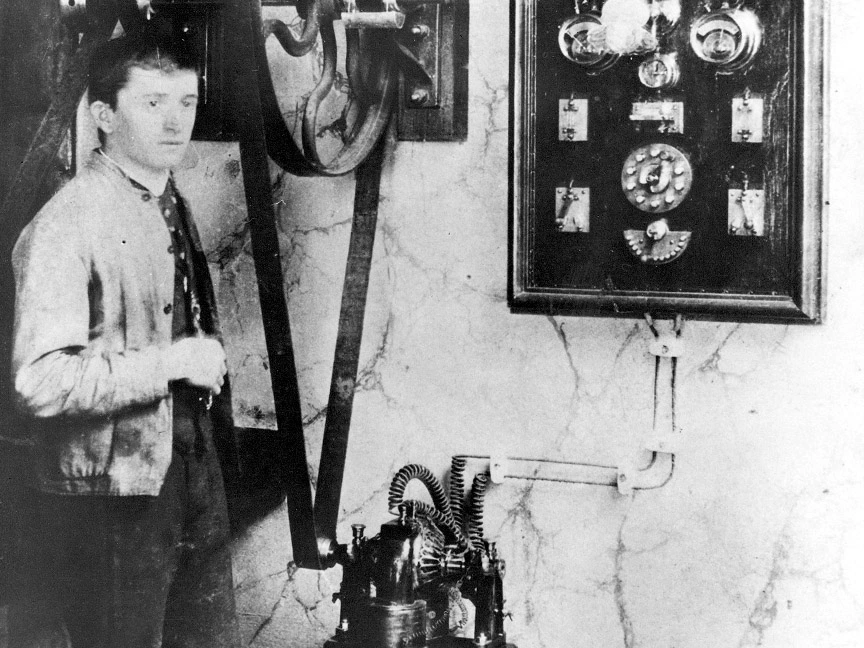

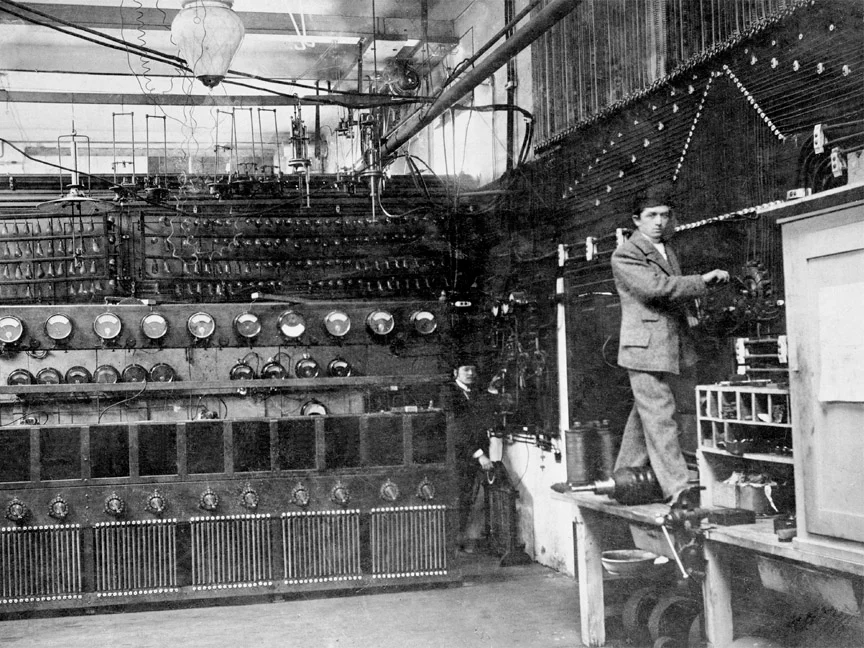
Career Beginnings.
Ferdinand Porsche's professional journey took off when he joined the Vienna-based electrical firm, Bela Egger & Co., in 1893. There, he contributed significantly to the development of electrical equipment and quickly rose through the ranks. His talent and dedication earned him the role of technical director at a young age.
Automotive Innovations.
In 1900, Porsche designed the Egger-Lohner C.2 Phaeton, also known as the - P1. This vehicle is considered the world's first hybrid car, featuring an electric motor integrated into a traditional internal combustion engine. The P1 showcased Porsche's forward-thinking approach to automotive engineering and foreshadowed his future achievements.
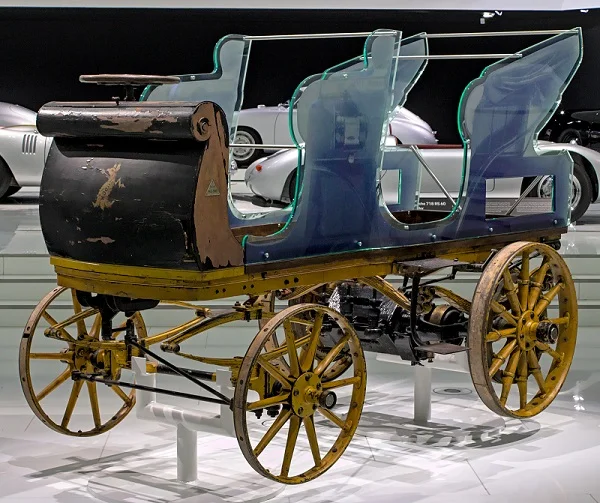

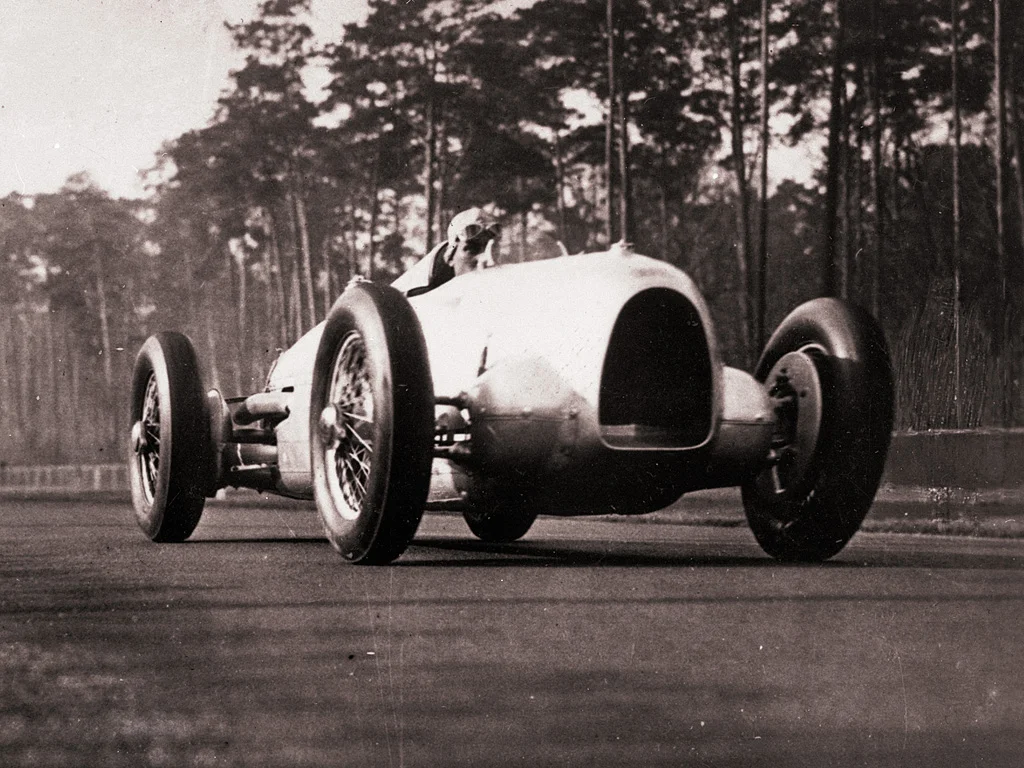
Stuttgart and Austro-Daimler.
In 1923, Ferdinand Porsche moved to Stuttgart, Germany, to take on a role at Daimler-Motoren-Gesellschaft (DMG). During his tenure at DMG, he worked on various projects, including designing a high-performance sports car that would later be known as the Mercedes-Benz SSK. Despite his notable work, disagreements with management led to his departure from DMG. In 1931, Porsche founded his own engineering consulting firm, Porsche Büro, which catered to various clients in the automotive industry. During this time, he collaborated with Auto Union (the predecessor of Audi) and designed the innovative Auto Union Type A Grand Prix race car. This car featured a rear-mounted engine, a concept that Porsche would revisit in his future endeavors.
The Volkswagen Beetle.
One of Ferdinand Porsche's most enduring legacies is his involvement in the creation of the Volkswagen Beetle, often referred to as the - People's Car. In the 1930s, Adolf Hitler, then Chancellor of Germany, envisioned a vehicle that could be affordable and accessible to the masses. He commissioned Porsche to develop this concept, and the result was the iconic Beetle, officially known as the Volkswagen Type 1. Production of the Beetle began in the late 1930s, but due to the outbreak of World War II, civilian production was limited. After the war, the Beetle gained global popularity and became one of the best-selling cars in automotive history, cementing Porsche's reputation as a visionary engineer.
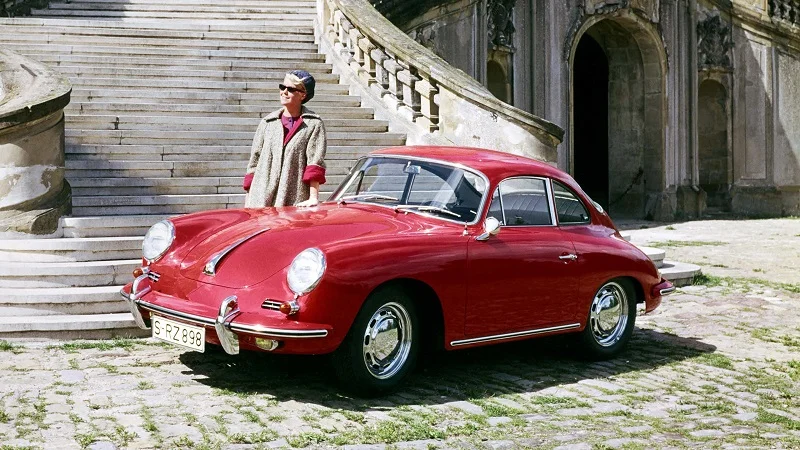


The Porsche 356 and Porsche AG.
In 1948, Ferdinand Porsche's son, Ferry Porsche, brought his father's dream to life by unveiling the Porsche 356, the first production car to bear the Porsche name. The Porsche 356 was a lightweight, rear-engine sports car that embodied the principles of performance, agility, and innovation that would become synonymous with the Porsche brand. The success of the Porsche 356 led to the establishment of Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche GmbH in 1949, which later evolved into Porsche AG. The company continued to create iconic sports cars, including the Porsche 911, which remains one of the most recognizable and coveted sports cars in the world.
Legacy and Impact.
Ferdinand Porsche's legacy extends far beyond the cars that bear his name. His innovative engineering and design principles have influenced the entire automotive industry. His concept of a rear-mounted engine and lightweight chassis is still evident in many sports cars today. Furthermore, the Porsche brand has become synonymous with high-performance, precision engineering, and driving pleasure. The company's continued success is a testament to Ferdinand Porsche's pioneering vision and commitment to excellence.
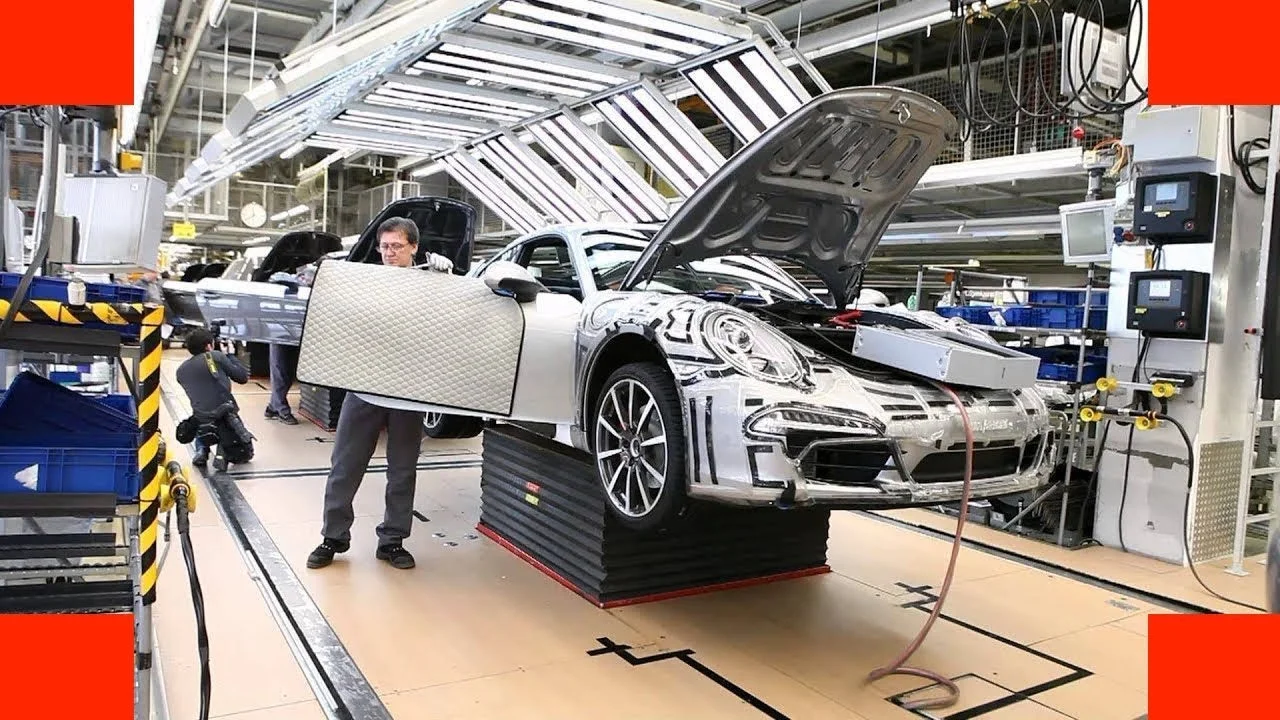


Conclusion.
Ferdinand Porsche's impact on the automotive world is immeasurable. From his early innovations and contributions to the development of electric and hybrid vehicles to his iconic designs like the Beetle and the Porsche 911, he transformed the way people think about cars. His dedication to engineering excellence and his passion for pushing the boundaries of automotive technology have shaped the industry for generations to come. Ferdinand Porsche's enduring legacy continues to inspire engineers, designers, and automotive enthusiasts worldwide, as his innovations continue to grace the roads and racetracks, carrying his name and vision into the future.
eXus Dev 27.7.2023







































